Downloads / case reports
Clinical and observational studies
Preclinical
Cold Atmospheric Plasma Promotes the Immunoreactivity of Granulocytes In Vitro
Kupke LS, Arndt S, Lenzer S, Metz S, Unger P, Zimmermann JL, Bosserhoff AK, Gruber M, Karrer S. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Promotes the Immunoreactivity of Granulocytes In Vitro. Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 17;11(6):902. doi: 10.3390/biom11060902. PMID: 34204360; PMCID: PMC8235417.
“The cell biological results of the study on the mouse model show that the change in immunoreactivity could be an important supporting mechanism for the CAP-induced improvement in wound healing. ”
Summary:
Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) reduces bacteria and interacts with tissues and cells, thus improving wound healing. The CAP-related induction of neutrophils was recently described in stained sections of wound tissue in mice. Consequently, this study aimed to examine the functionality of human polymorphonuclear cells (PMN)/granulocytes through either a plasma-treated solution (PTS) or the direct CAP treatment with different plasma modes and treatment durations. In conclusion, the modification of PMN immunoreactivity may be a main supporting mechanism for CAP-induced improvement in wound healing.
Read More
Preclinical
Non-invasive Physical Plasma Modulates Macrophage Polarization: A Potential Strategy for Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling
Niu Y, Förster S, Badendieck S, Nokhbehsaim M, Abazid A, Stope MB. Non-invasive Physical Plasma Modulates Macrophage Polarization: A Potential Strategy for Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling. Anticancer Res. 2024 Jun;44(6):2437-2444. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17050. PMID: 38821624.
“Cell morphology, viability, and proliferation were not affected by up to 6 minutes of NIPP treatment.”
Dr. M. Stope, Department of Gynecology and Gynecological Oncology, University Hospital Bonn
Summary:
Non-invasive physical plasma (NIPP) has shown promise in the treatment of cancer. However, conflicting results have been reported regarding the effect of NIPP on macrophage polarization. As tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are essential in the regulation of cancer development, this study aimed to determine the role of NIPP treatment in macrophage polarization and tumor-microenvironment (TME) remodeling. No significant changes were observed in temperature and pH value after NIPP treatment, while the formation of hydrogen peroxide was promoted in a time-dependent manner. Cell morphology, viability, and proliferation were not affected by up to 6 minutes of NIPP treatment.
Read More
Dermatology/Aesthetic
Other Indications
Non-invasive physical plasma for preventing radiation dermatitis in breast cancer: Results from an intrapatient-randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial
Dejonckheere CS, et al. Non-invasive physical plasma for preventing radiation dermatitis in breast cancer: Results from an intrapatient-randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 Nov 4;44:100699. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100699. PMID: 38021092; PMCID: PMC10654149.
“The data suggest the potential benefit of NIPP in RD prevention. A randomised trial with a physical control group is warranted to confirm these promising results (DRKS00026225).”
Dr. Dejonckheere, Department of Radiation Oncology, University Hospital Bonn
Summary:
To investigate the effect of topical non-invasive physical plasma (NIPP), a volatile mix generated out of ambient air, on prevention of acute radiation dermatitis (RD) during and after whole-breast irradiation (WBI). Sixty-four patients were included. There were no significant differences between breast halves. Tolerability of NIPP was excellent and side effects were not observed. Even though there were no differences between intrapatient-randomised breast halves, the overall incidence and severity of acute radiation-induced skin toxicity were considerably lower when compared to a prospectively collected SoC cohort. Our data suggest the potential benefit of NIPP in RD prevention. A randomised trial with a physical control group is warranted to confirm these promising results (DRKS00026225).
Read More
Chronic Wounds
Cold plasma treatment for hard-to heal wounds
Gebhardt, Ascher. Cold plasma treatment for hard-to heal wounds. mecial-special (2022)
“The present cases show good tolerability of cold plasma therapy as well as clear indications
of the wound healing-promoting effect.”
Gebhardt/Ascher
Summary:
Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) is increasingly being used to stimulate the healing of wounds that are difficult to heal. In the present case study, 12 patients with chronic wounds, some of which had been present for over a year, were treated with KAP. A significant reduction in wound size and a reduction in the pH value within the wound was observed.
Read More
What experts say about the CAP-therapy with the plasma care®
Salesfolder plasma care®
Whitepaper plasma care®
Scientific information and case reports about CAP and treatment with plasma care®
Whitepaper plasma derma care®
Information material for download:
“
"We use plasma care® as a complementary therapy to support rapid wound healing and prevent infection."
Johannes Schwaiger
CEO Ellipsa, Regensburg
"I use the plasma care for wound treatment with DFS and chronic ulcers and have noticed a good supporting effect on many wounds. Cold plasma therapy is a promising approach to standard care."
Dr. Nikolaus Scheper, Marl
Specialist Diabetology
"The cold plasma can be used from day 1 (exudation phase) to the last day (epithelisation/scar formation). The application is very simple because the device is very handy and small"
Rahel Wyss
Woundmanager Swizterland
Case reports
Wound healing disorders
The plasma care® has been used in more than 30,000 treatments since 2019. In our case reports, the plasma care® was used for cold plasma therapy.
Minor Wounds
Initial situation:
Patient, 39 years, healthy and active in sports. Blister formation in the ski boot leads to an open, weeping, painful blister.
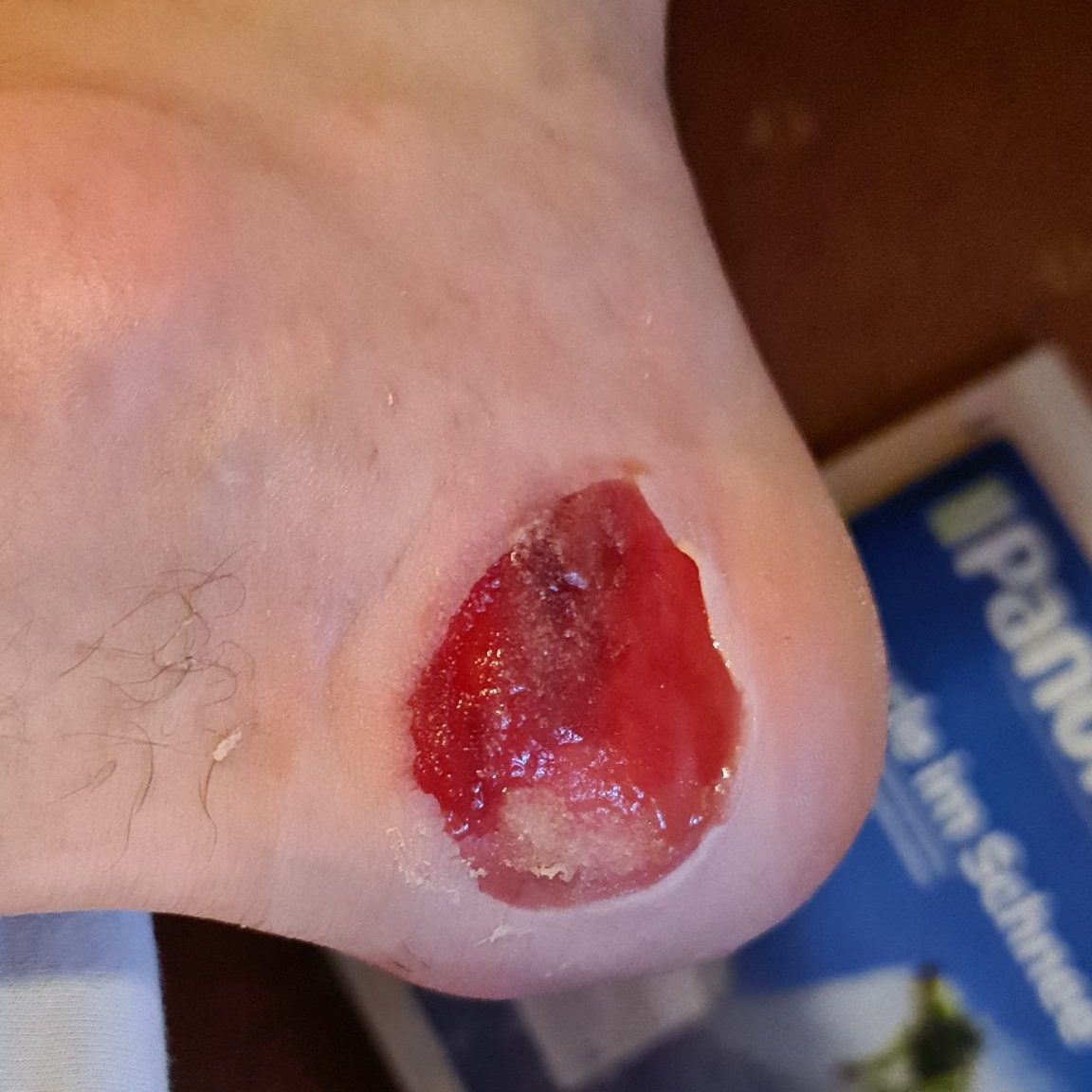
Tag 0
Start of treatment
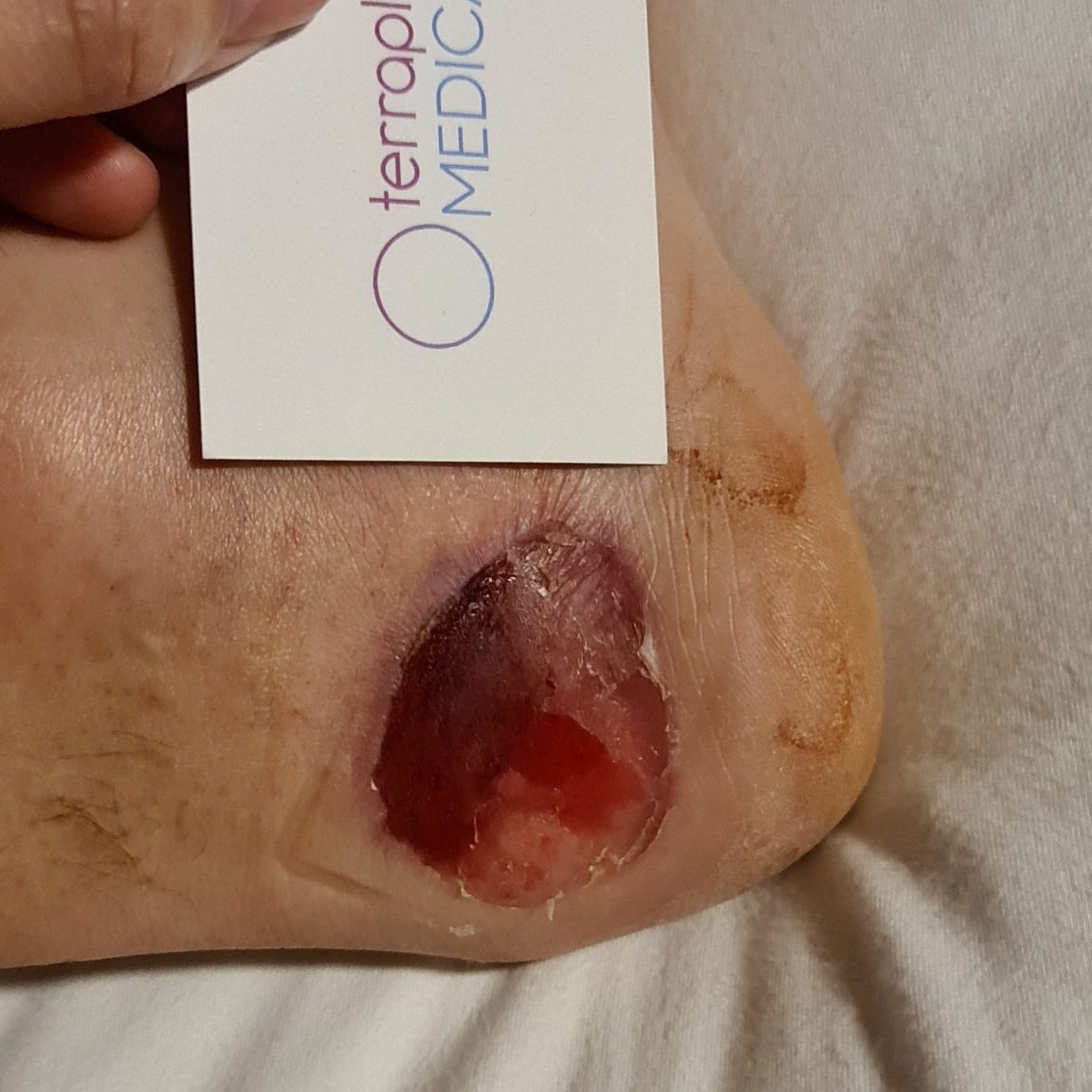
Tag 2
1 CAP treatment
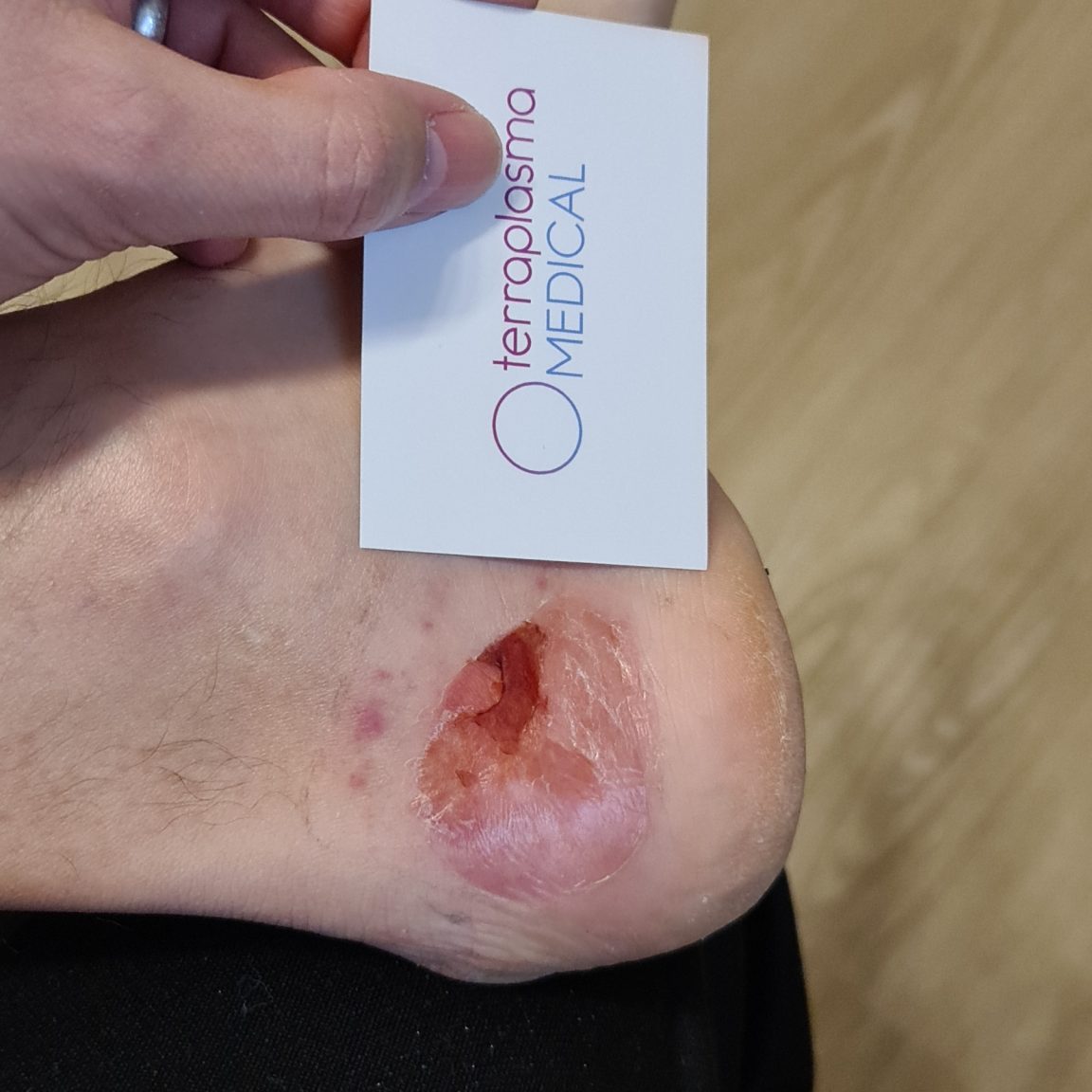
Tag 4
2 CAP treatments
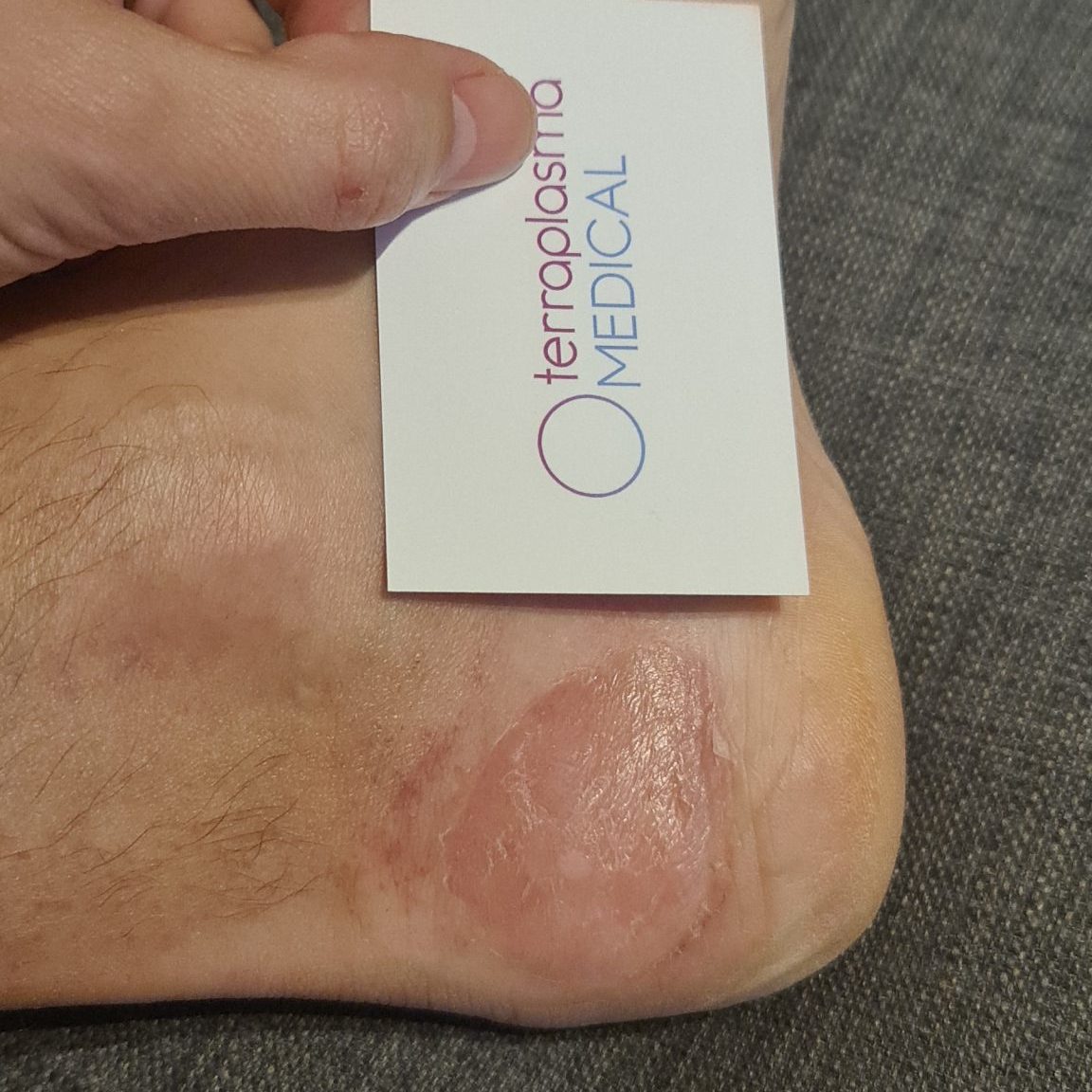
Tag 7
3 CAP treatments
Treatment overview:
Treatment 4 days, 1 min, wound covered with hydrocolloid dressing. During the entire treatment, the wound was still under strong mechanical stress – the patient was able to continue skiing.
Postoperative wound healing disorder stump
Initial situation:
Patient (63 years, female): traumatic transtibial amputation, postoperative wound healing disorder on the residual limb (bearing surface of the prosthesis) following flap plastic surgery, wound has existed for 1.5 years, no infection.
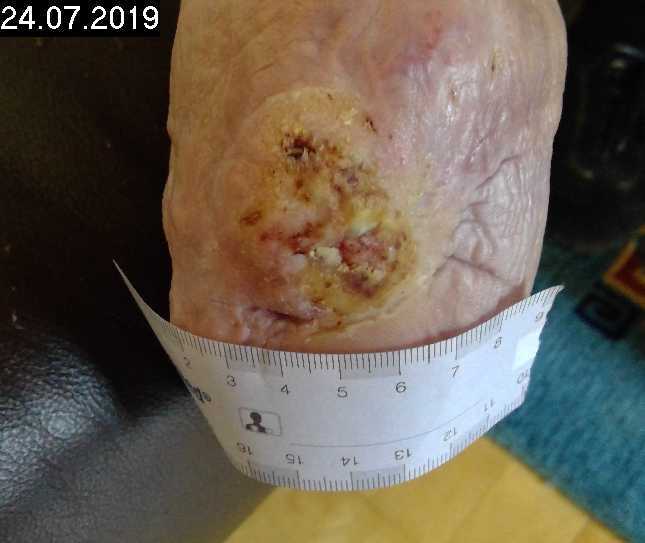
Tag 0
Start of treatment
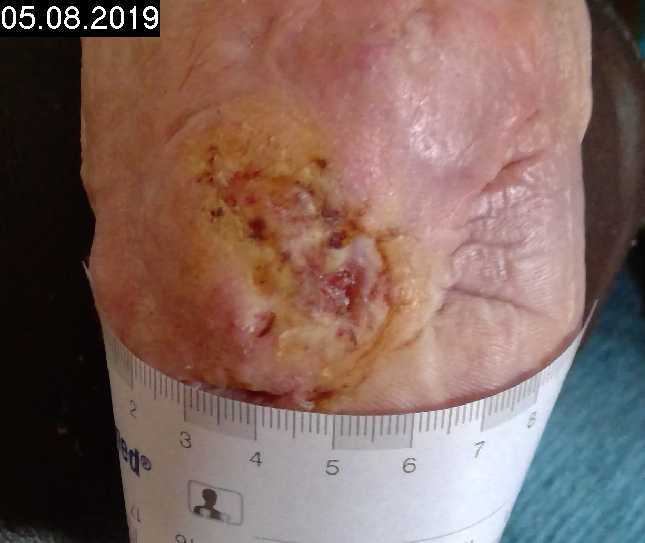
Tag 3
2 CAP treatments
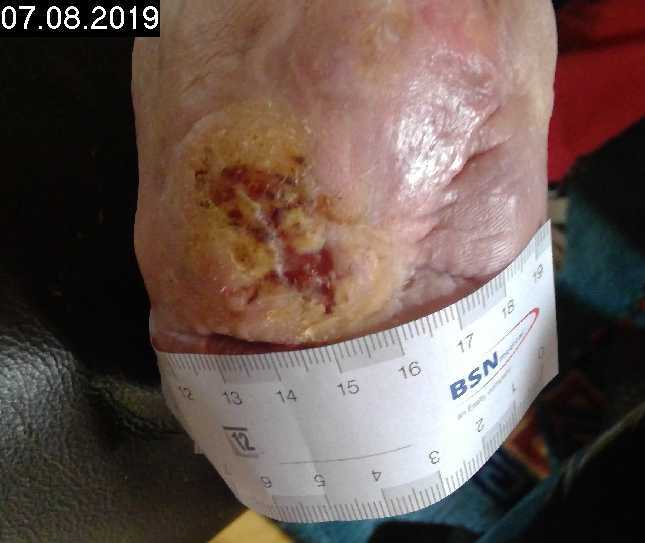
Tag 7
3 CAP treatments
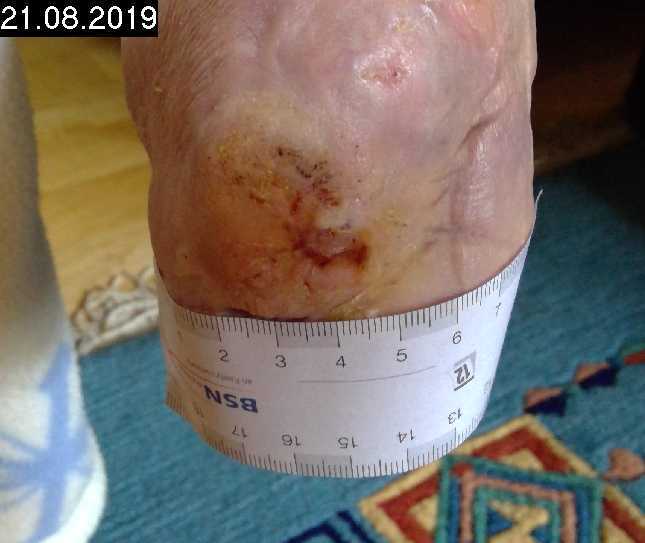
Tag 16
6 CAP treatments
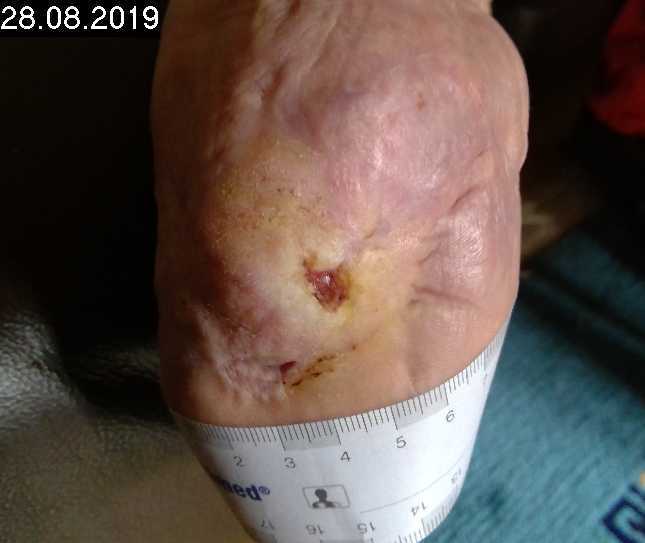
Tag 25
9 CAP treatments
Treatment overview:
9 treatments (1 min/13 cm²) performed within three and a half weeks. Reduction of wound size from 2.04 cm x 1.87 cam to 0.48 cm x 0.51 cm.
Postoperative wound healing disorder split skin graft and flapplasty
Initial situation:
Patient (77 years, female): secondary healing wound (split house graft and flap plasty) after trauma (crush injury in car accident); wound healing disorder in the presence of known CVI and heart failure, infection with Enterobacter aerogenes, tendency to edema formation in the lower legs.
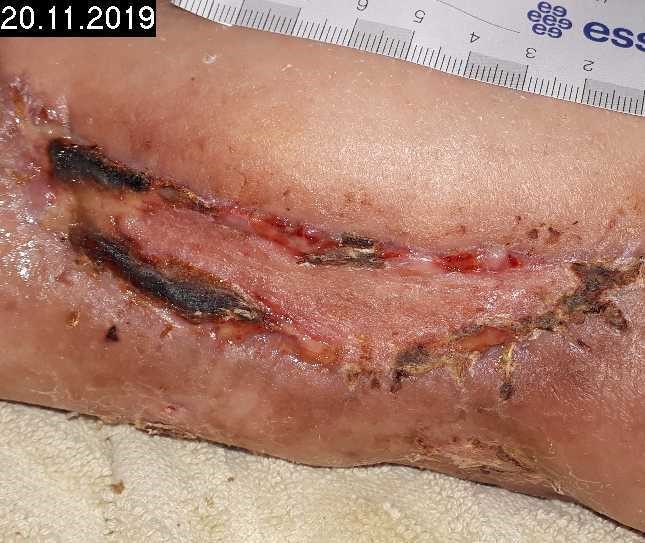
Woche 0
Start of treatment
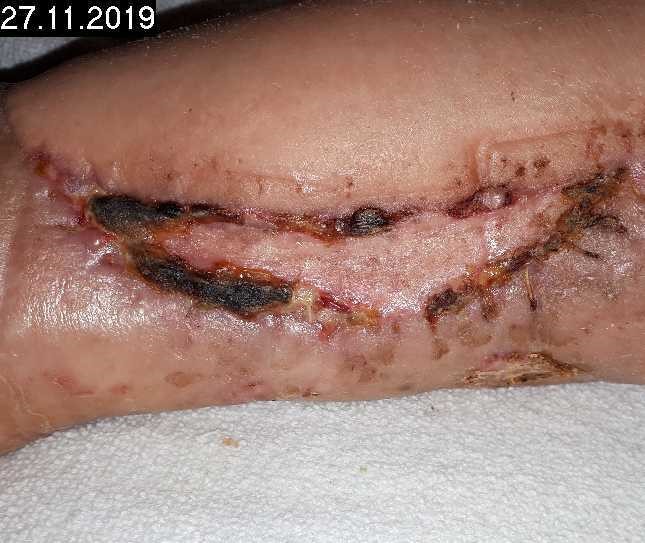
Woche 1
3 CAP treatments
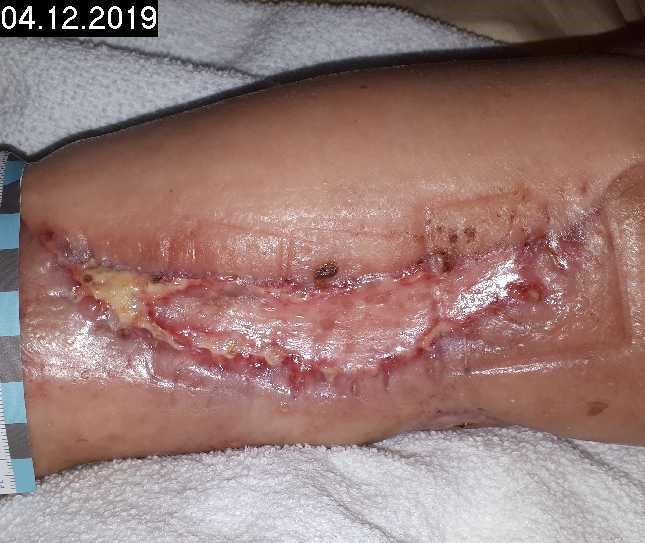
Woche 2
5 CAP treatments
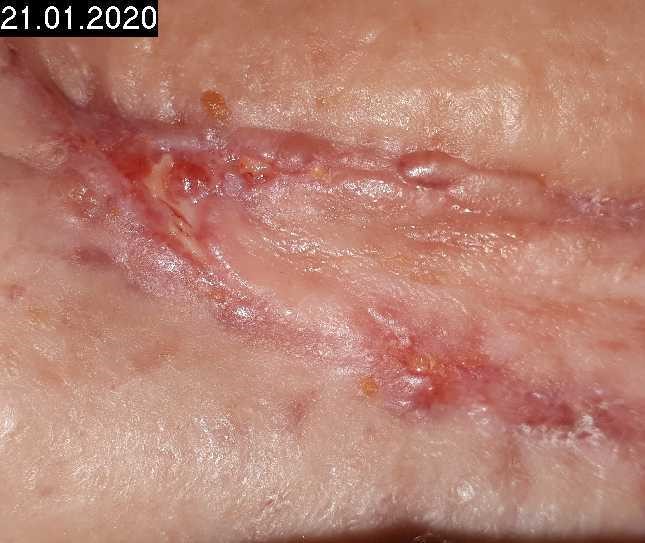
Woche 8
14 CAP treatments
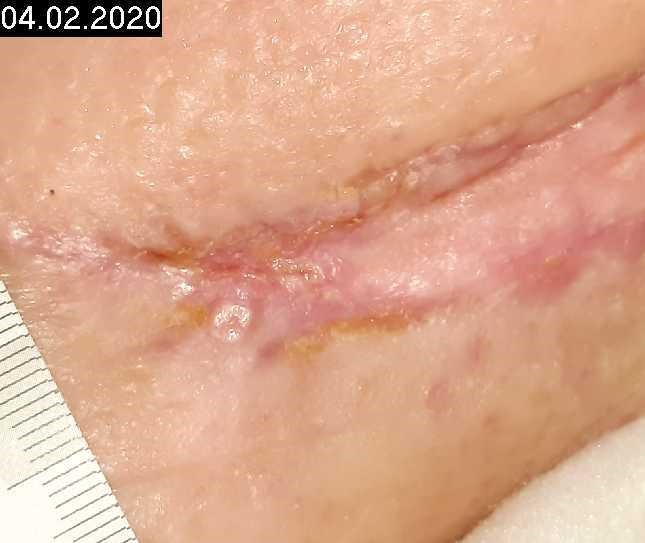
Woche 11
18 CAP treatments
Treatment overview:
2 x per week cold plasma treatments (1 min), additional switch to moist wound care to soften incrustations and necroses as well as regular mechanical cleansing, after 18 treatments in 11 weeks except for punctual superficial skin opening (wound size: 0.22 x 0.17 cm), wound completely epithelialized. Plasma therapy no longer necessary.
Postoperative wound healing disorder after osteosynthesis in a dislocated humerus fracture in a 28-year-old female patient.
Initial situation:
28-year-old female patient, without concomitant diseases, WHS after plate osteosynthesis, WHS occurred after suture removal with purulent secretion. Patient has plaster allergy.
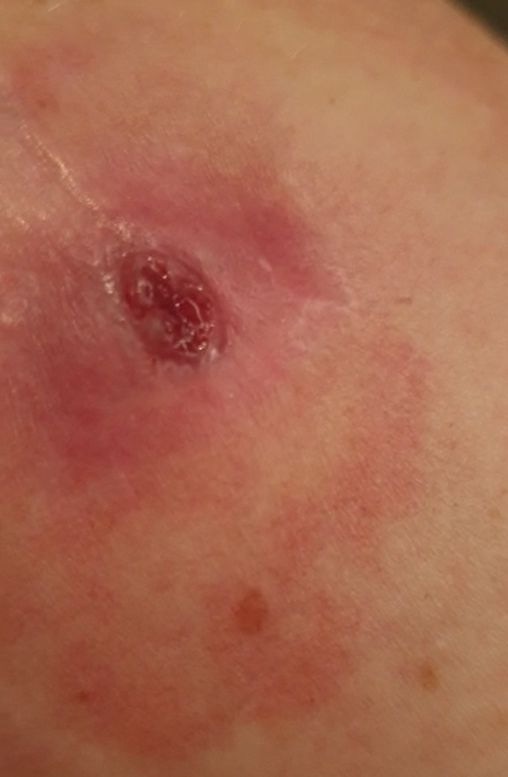
Tag 0
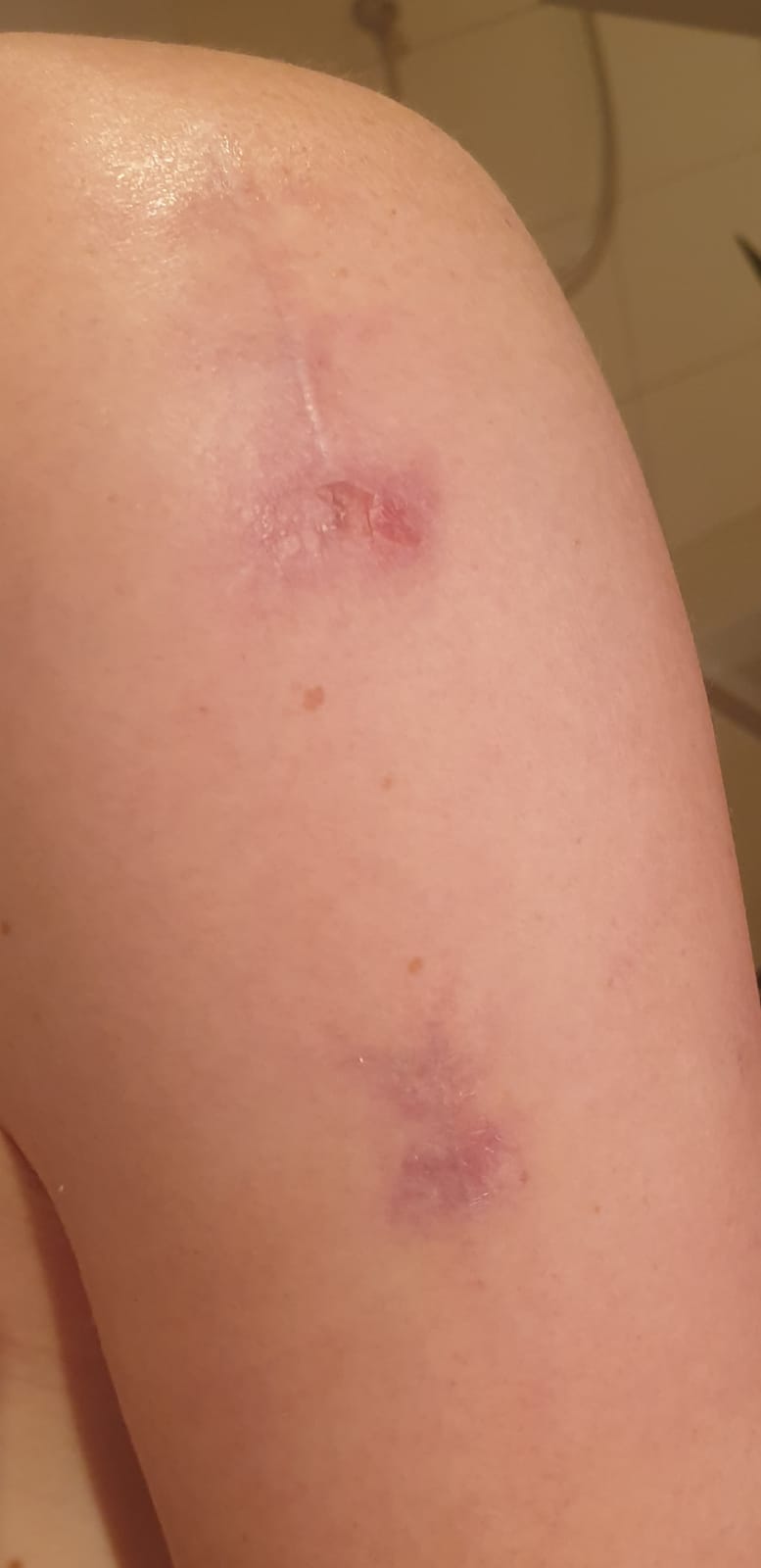
Abbildung 2
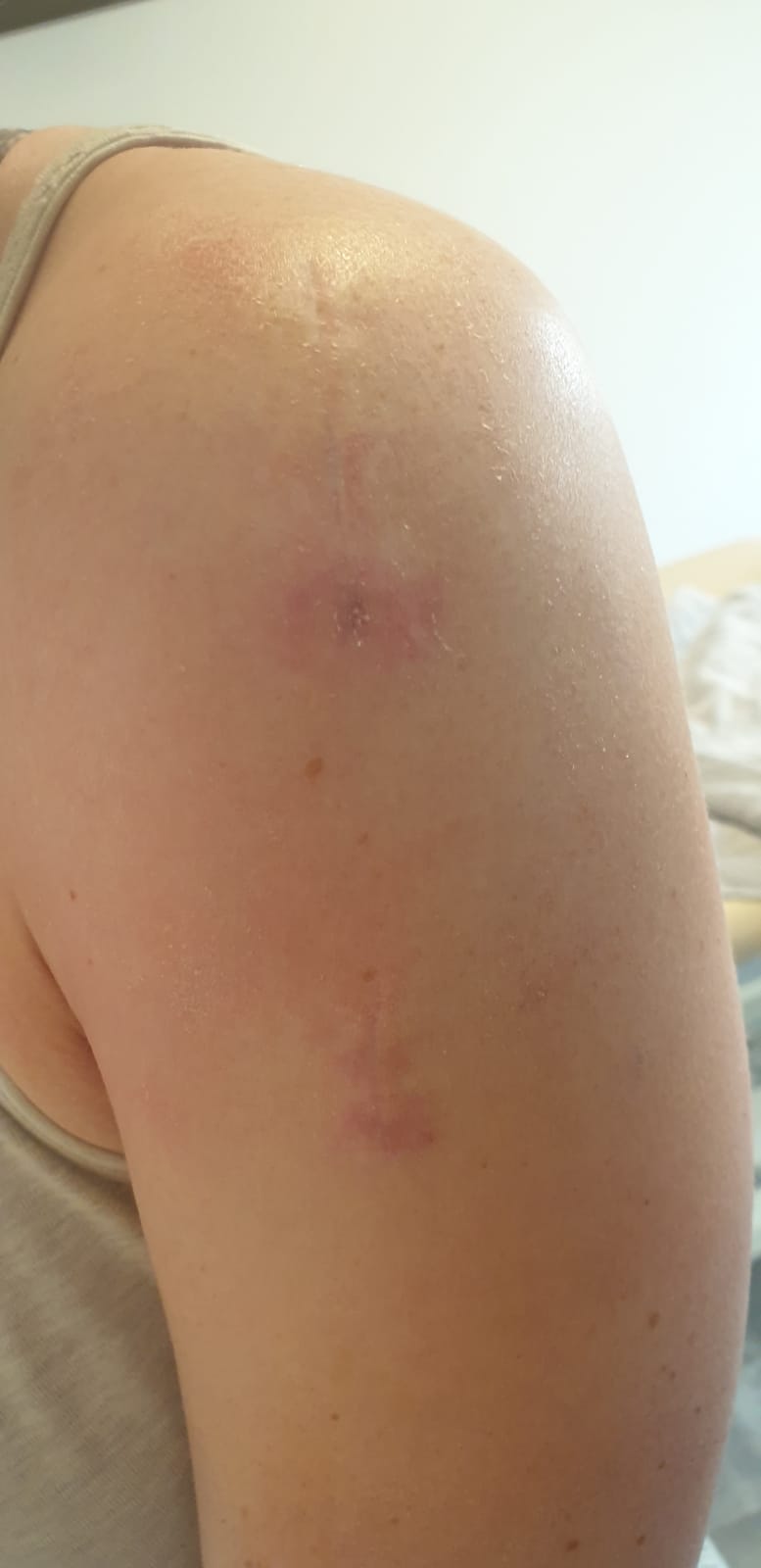
nach 3 Wochen
Treatment overview:
Treatment daily, 3 minutes. After one week, significant improvement: no more signs of infection and pain. After another 3 days the wound was healed.
Chronic wounds
DFS with pAVK
Initial situation:
Patient (78 years) with diabetes mellitus, progressive polyneuropathy and pAVK develops ulcer III degree, toe dome right foot
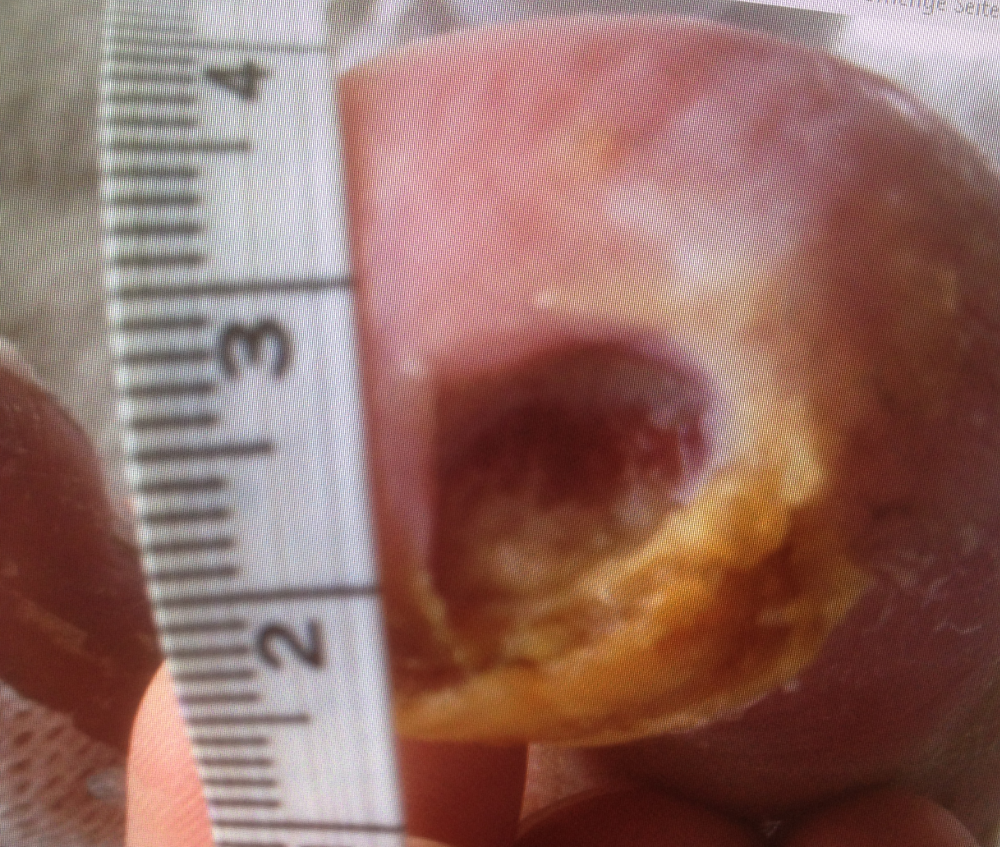
Figure 1
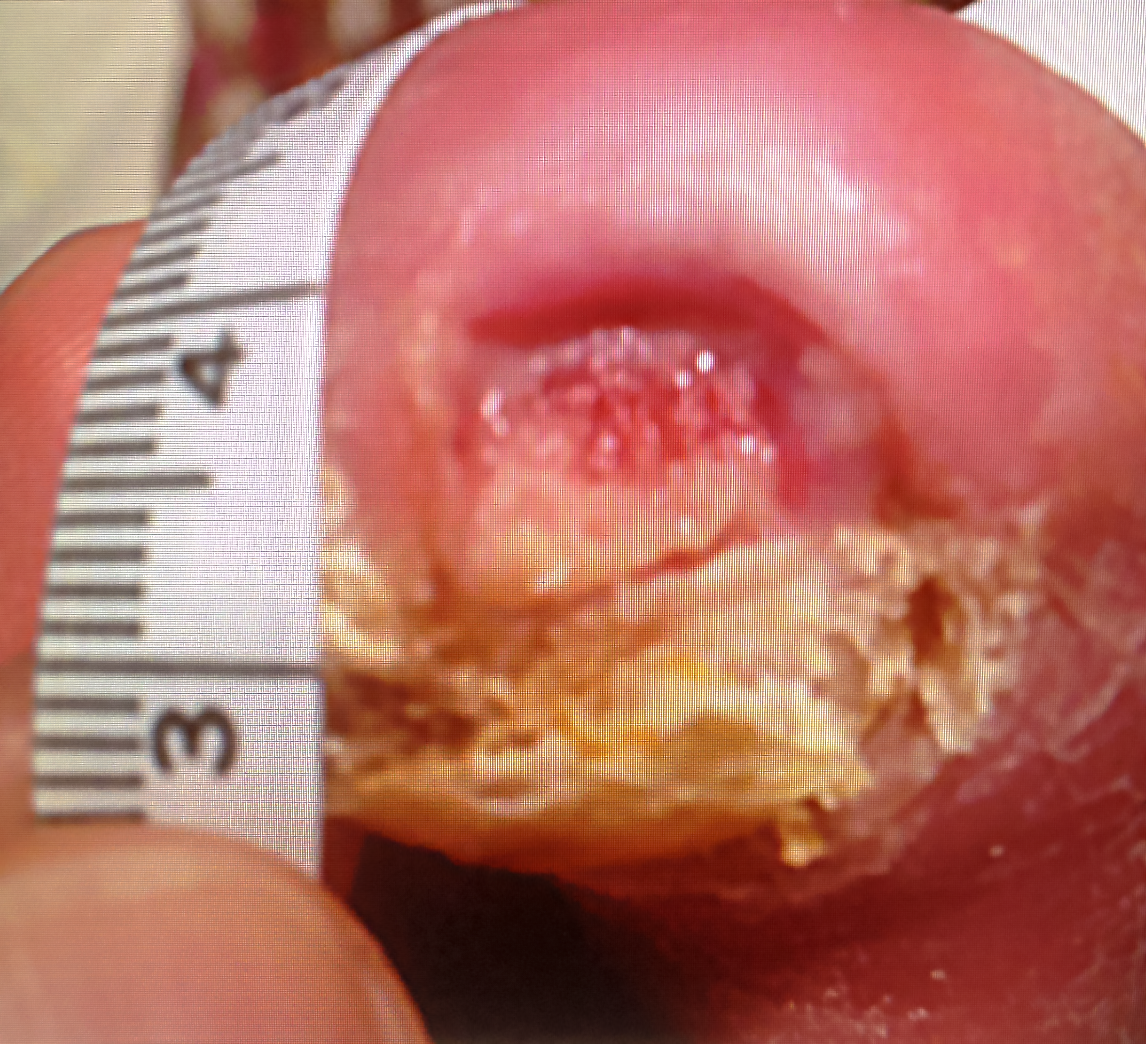
Figure 2
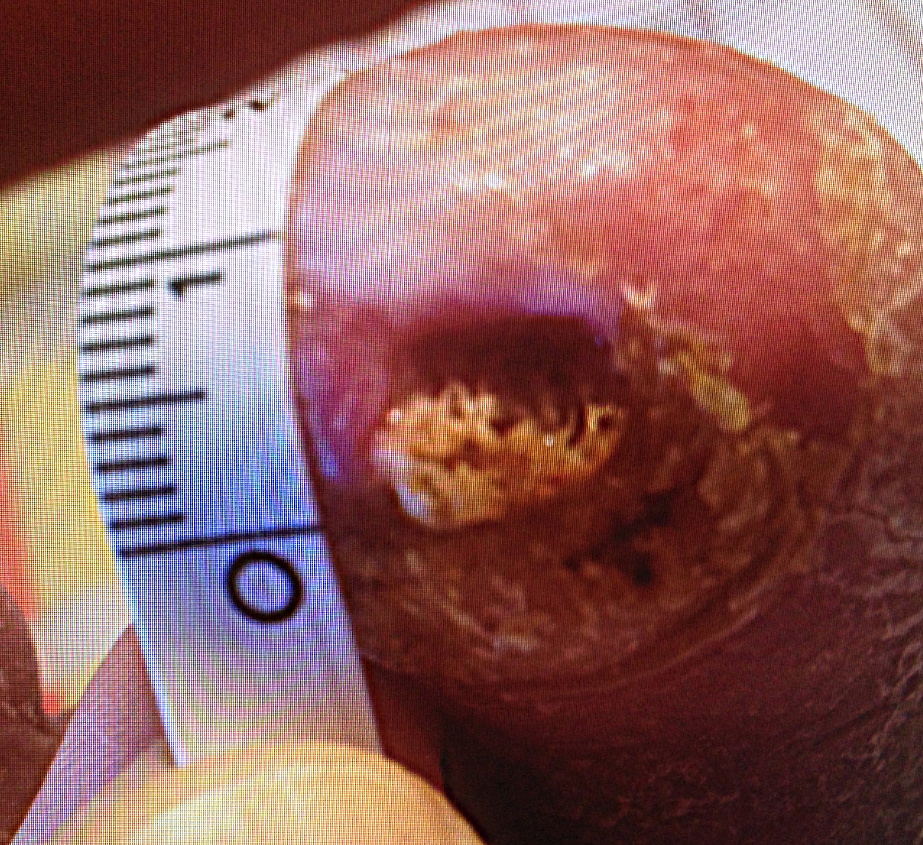
Figure 3
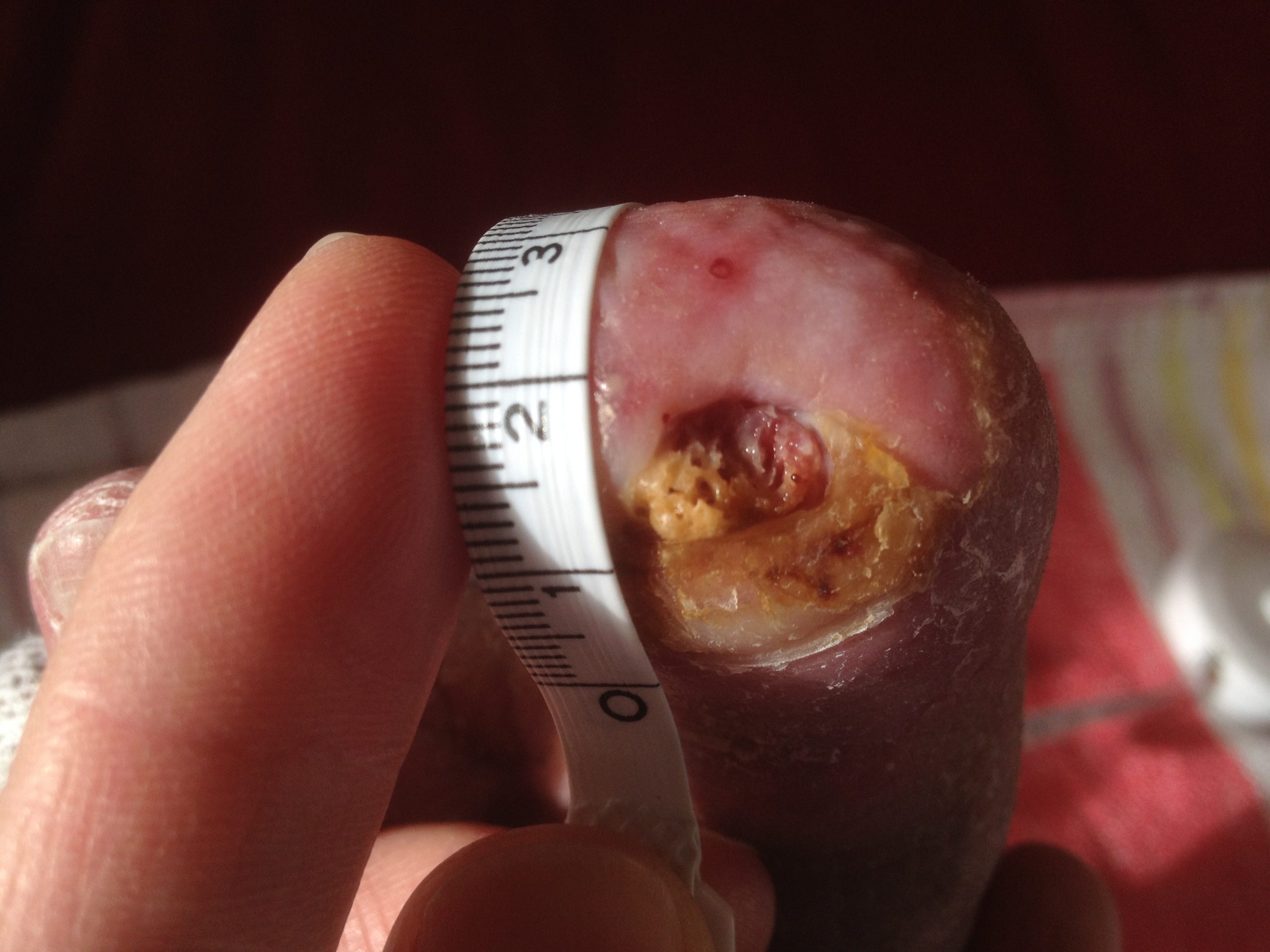
Figure 4
Treatment overview:
2 treatments per week, 2 minutes. After 14 days the wound was significantly more vital, after 6 weeks the PHMB foam dressing could be replaced by a polyretan dressing. After a total of 39 treatments, the sore had significantly reduced, KAP therapy was discontinued with stable wound conditions and adapted shoe care.
DFS
Initial situation:
Patient (50 years, male): Diabetes mellitus type II, diabetic foot syndrome; borderline amputation of the 4th toe on the left. Wound infection with partially resistant corynebacteria, enterococci and staphylococci.
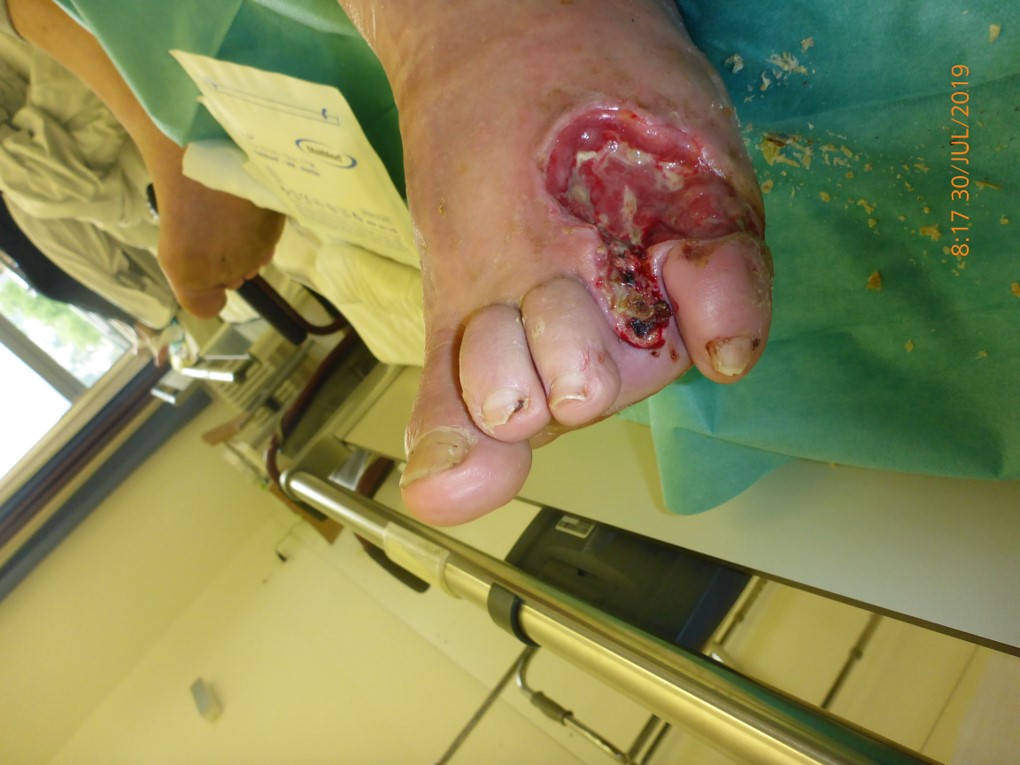
Tag 0
Start of treatment
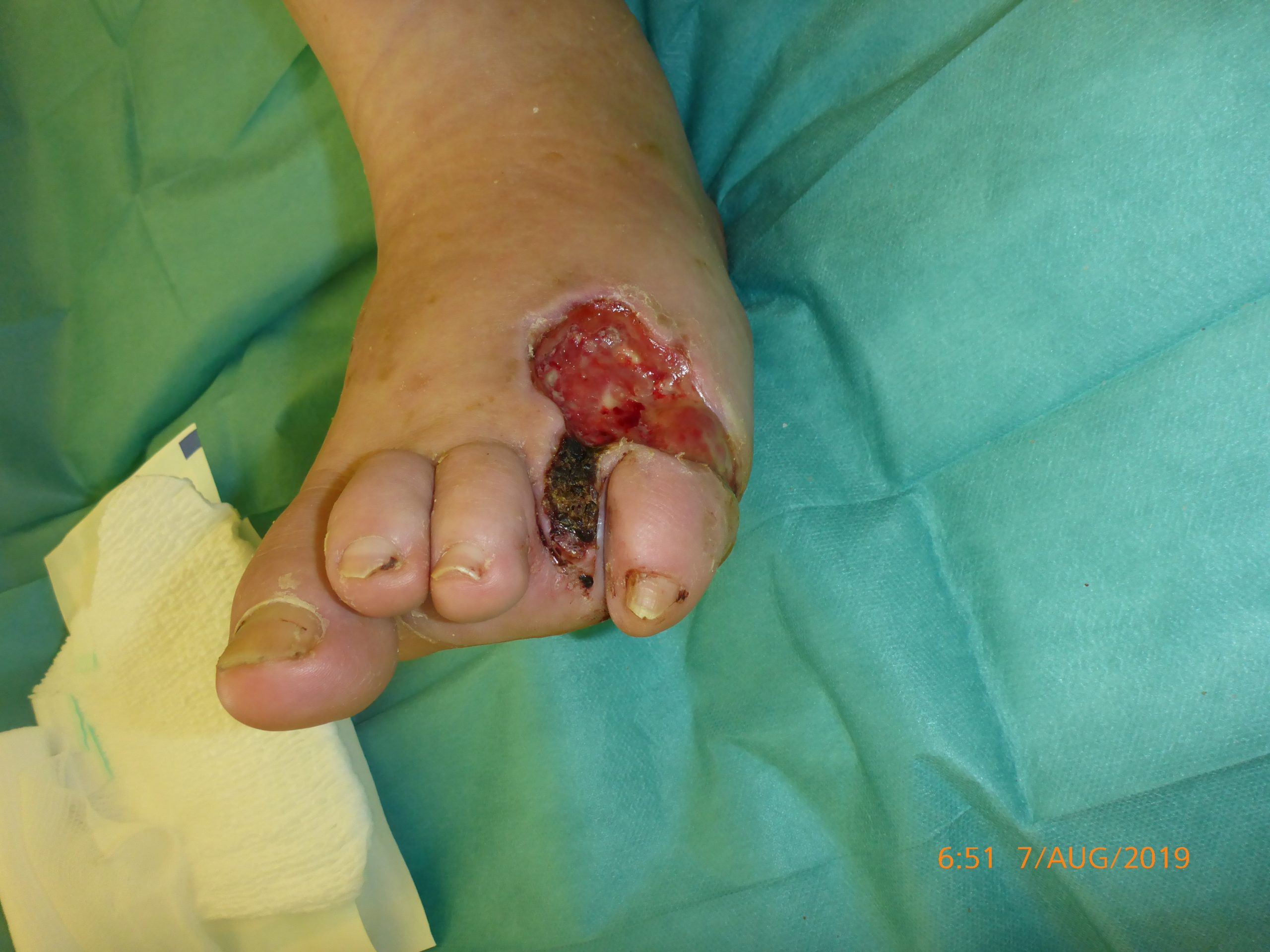
Tag 2
2 CAP treatments
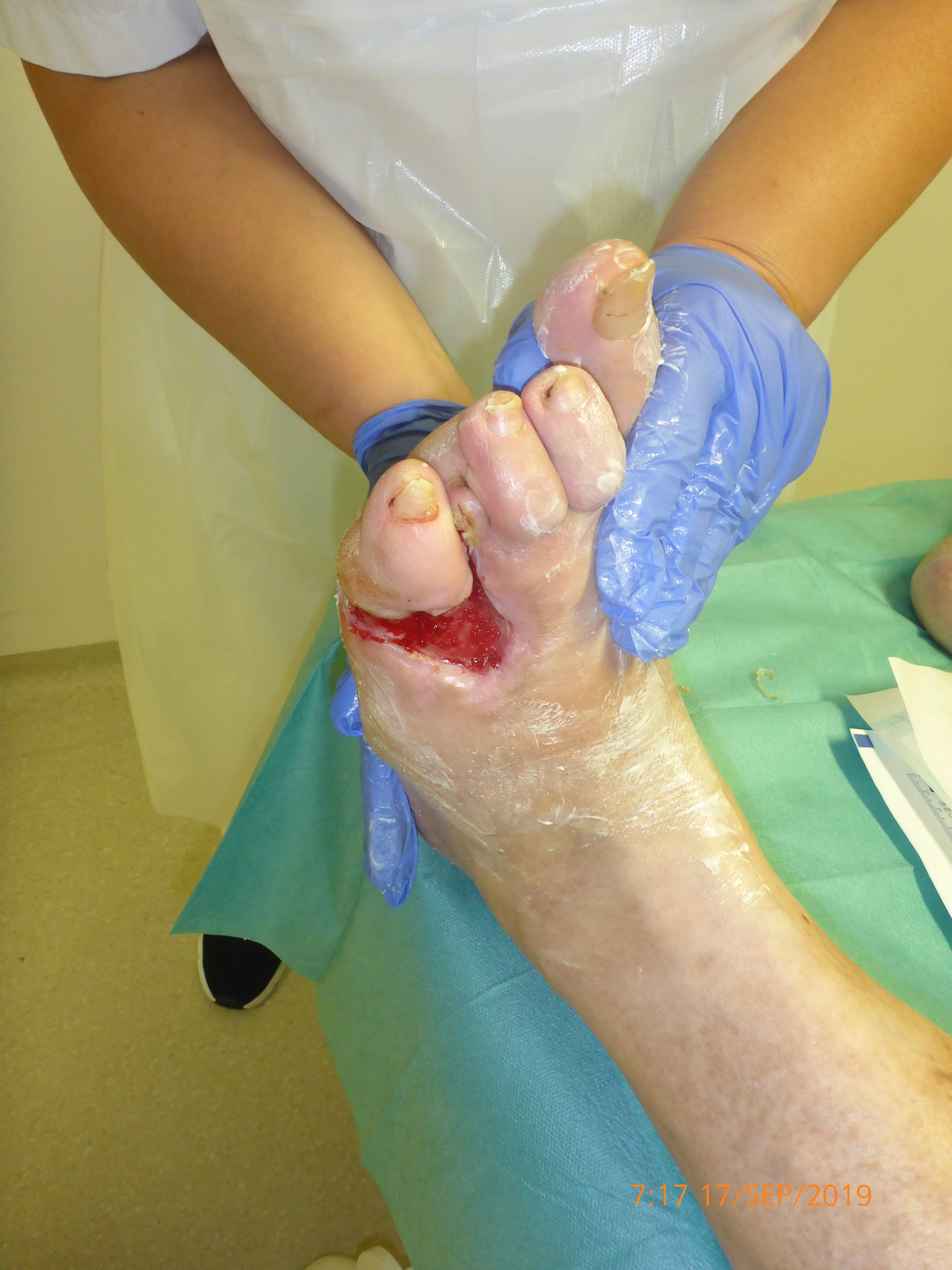
Tag 14
4 CAP treatments
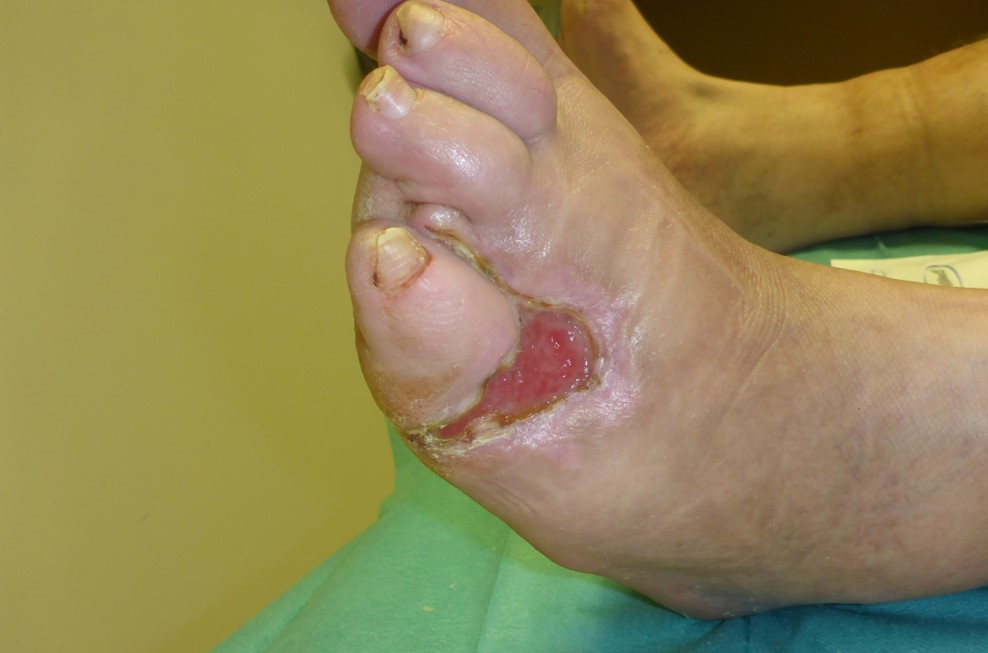
Tag 42
7 CAP treatments
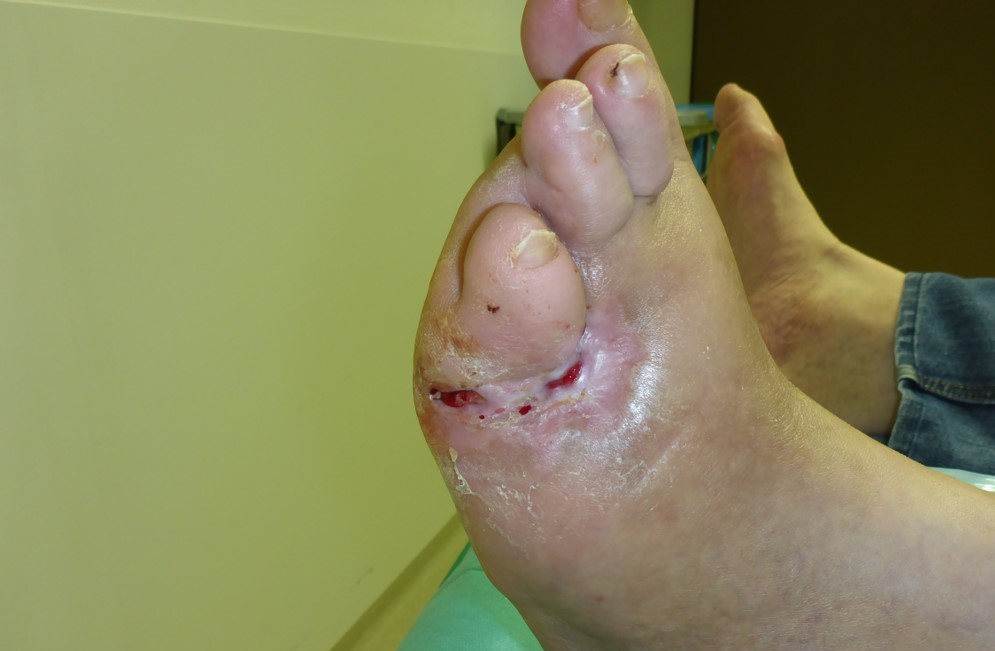
Tag 83
9 CAP treatments
Treatment overview:
2 treatments / week in the first 3 weeks, then 1 treatment every 2 – 4 weeks (9 treatments in 12 weeks) as part of the dressing change in the clinic.
Healing after the start of plasma therapy and with optimal wound treatment with surgical debridement, relief, appropriate dressing, etc.
Sacral decubitus in paraplegia
Initial situation:
Patient (59 years, male): Active patient with paraplegia, pressure ulcer in the area of the due to frequent swimming and sweating. After 14 months without healing, the wound was 3.5 x 3 cm with heavy fibrin coating.
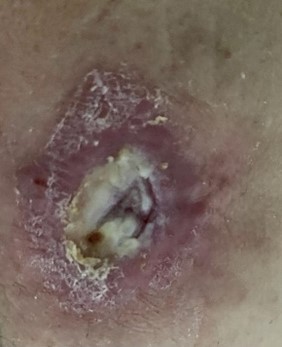
03.08.2021
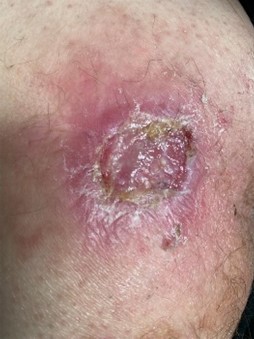
05.08.2021
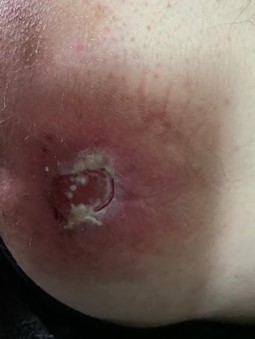
18.08.2021
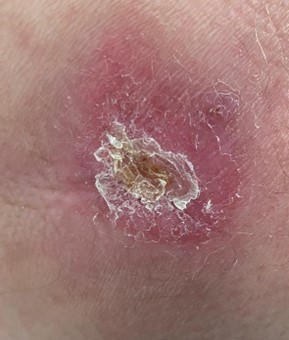
02.09.2021
Treatment overview:
2 times 2-min. treatment, already after the 2nd treatment the fibrin coatings came off, the redness decreased. After 2 weeks significant reduction to 2 x 2 cm, granulation starts. Complete healing after 5 weeks.
Ulcus cruris
Initial situation:
Patient (77 years, female): Bedridden due to a spinal injury. Recurrence of a leg ulcer of unclear origin on the right lower leg, no edema, vessel structure unclear. Wound healing stagnated for several months, partly purulent coatings, patient reports severe pain during mechanical wound cleaning.
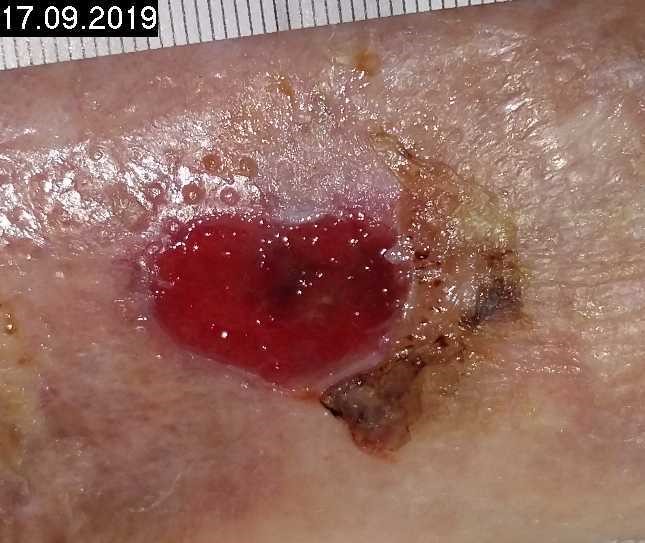
Woche 0
Start treatment
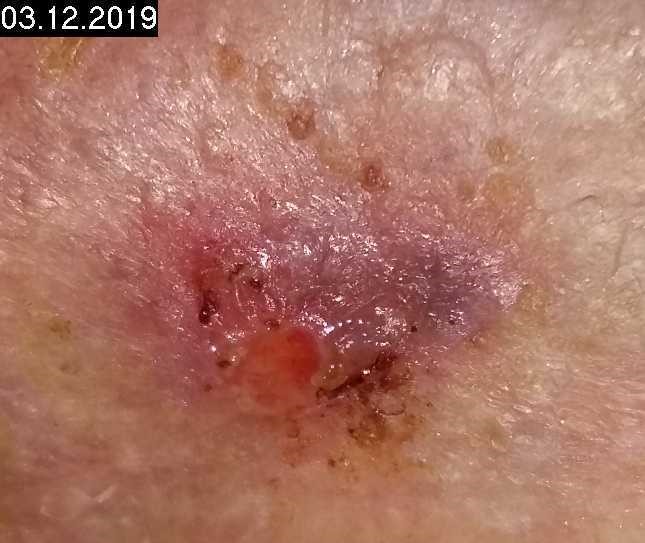
Woche 4
1. Treatment interval / 8 CAP treatments
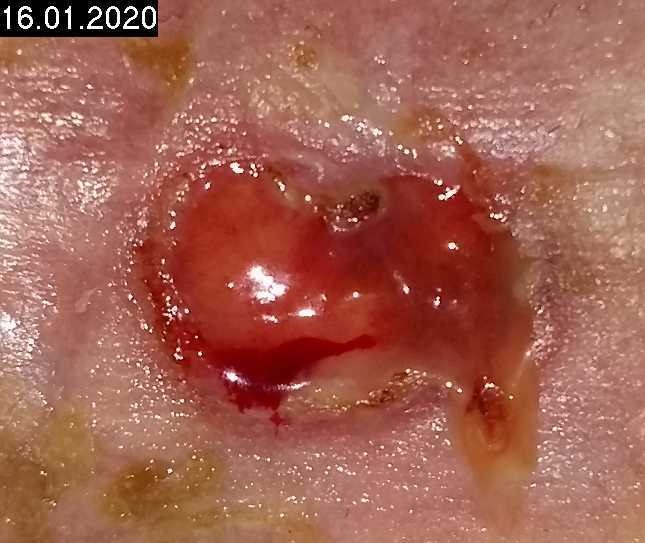
Woche 10
Recurrence
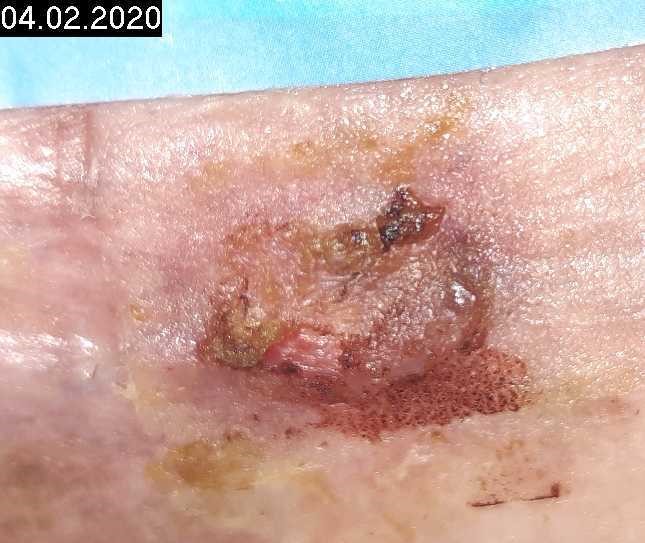
Woche 14
2. Treatment interval / 8 CAP treatments
Treatment overview:
8 cold plasma treatments (1 min) in 4 weeks lead to a significant reduction in wound size, progressive epithelialization, reduction in pain, KAP was interrupted, recurrent ulcer occurred, cold plasma treatment was then resumed.
Complete epithelialization of the wound after 4 weeks of renewed cold plasma therapy (2 x week, 1 min).
"Treating hard-to-heal skin and nail onychomycosis of diabetic foot with plasma therapy"
Patient (80 years, female) with diabetes mellitus, history: amputation of the right foot below the knee and amputation of the left 4th toe three years ago. She got athlete’s foot on the left foot, treatment with antifungal ointment was unsuccessful for 4 weeks, as well as oral antifungal treatment with fosravuconazole-L-lysine ethanolate. The patient was then treated daily with cold plasma. After one week, the smears and the situation of the foot improved, the antifungal therapy was replaced with plasma therapy combined with moisturizing ointment. The patient could be discharged cured after 3 weeks.
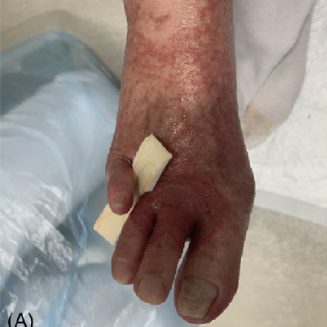
Week 0
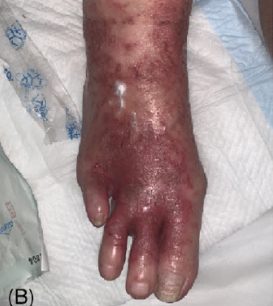
Week 1
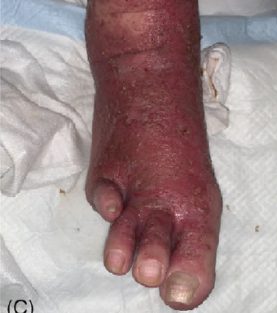
Week 2
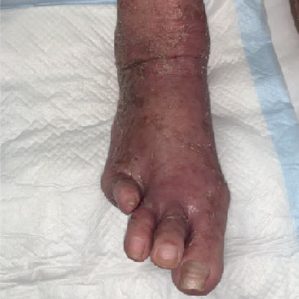
Week 3
Special clinic
Clinic University of Graz (A):
At LKH-Univ. Klinikum Graz, the complementary use of cold plasma is being tested with two devices for chronic wounds: at the Clinical Department of Cardiac Surgery and at the University Clinic of Dermatology and Venereology.
The report from the Department of Cardiac Surgery:
… Cures persistent infections in artificial heart patients.
Since May 2020, Cold Plasma has been applied at the Clinical Department of Cardiac Surgery to treat chronic driveline infections. Patients with left ventricular assist devices (LVAD, a so-called artificial heart) have a type of pump directly attached to the heart that helps it beat and is powered by a battery outside the body. Where the lead exits the heart, called the driveline, in the abdomen, it can cause persistent, chronic
infections, often with multi-resistant germs. If all other treatment options have been unsuccessful, these sites are treated with cold plasma. For the patients themselves, the treatment is completely painless and without side effects.
The report from Dermatology:
The Univ. Clinic for Dermatology has been using “plasmacare®” since June 2020, where it is also used on chronic wounds to reduce bacteria and biofilm in order to stimulate or improve wound healing. “We are currently in the testing phase and have used the device on three patients. The result was promising in all of them” reports dermatologist Barbara Binder. According to Binder, the areas of application are primarily in healing stagnation.
Find out more about the application of cold plasma
What ist cold plasma?
What is cold plasma?
Learn moreWound treatment
Wound treatment
Learn moreDermatology
Dermatology
Learn more
Contact & FAQ
Questions about cold plasma?
There are many questions surrounding cold plasma therapy: Which bacteria does cold plasma affect? How long does the therapy last? …. We have compiled the most frequently asked questions and answers for you here. You are also welcome to contact us directly.


